
Jeffery A. Hobden, PhD
Associate Professor of Microbiology, Immunology & Parasitology
Associate Professor of Microbiology, Immunology & Parasitology
2020 Gravier St
Lions Building, Room 744
New Orleans, LA 70112
jhobde@lsuhsc.edu

Hobden Lab, Summer 2010
Degrees
BS Biological Sciences - 1985
Loyola University, New Orleans
MS Medical Microbiology - 1988
Louisiana State University Medical Center, New Orleans
PhD Medical Microbiology - 1992
Louisiana State University Medical Center, New Orleans
Research Interests
As the average American grows older, the incidence of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis (accompanied by type 2 diabetes and obesity) will dramatically rise, resulting in an increasing number of prosthetic knee and hip joint implant procedures. A serious and costly complication of prosthetic joint implantation is infection. In acute prosthetic joint infection (PJI), irrigation and debridement with prosthesis retention is preferred, but not always curative. There is little information on what variables lead to treatment failure. One factor that likely contributes to a poor prognosis is the propensity of bacteria, especially Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), to form biofilms on implant surfaces. Bacteria growing in biofilms are difficult, if not impossible, to clear by the host immune response and recalcitrant to antibiotic therapy.
Dr. Hobden’s laboratory is currently developing clinically relevant model systems to gain an understanding of bacterial biofilm formation on various orthopedic substrates such as alloys of titanium, polymethyl methacrylate bone cement, and ultra-high density polyethylene. With these models, Dr. Hobden’s laboratory is examining the efficacy of various antimicrobials and intervention strategies to eliminate or prevent Gram-positive (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus [MRSA, coagulase-negative staphylococci]) and Gram negative (Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) clinical isolates from growing as a biofilm on orthopedic substrates.
Bacteriology can be quite colorful!
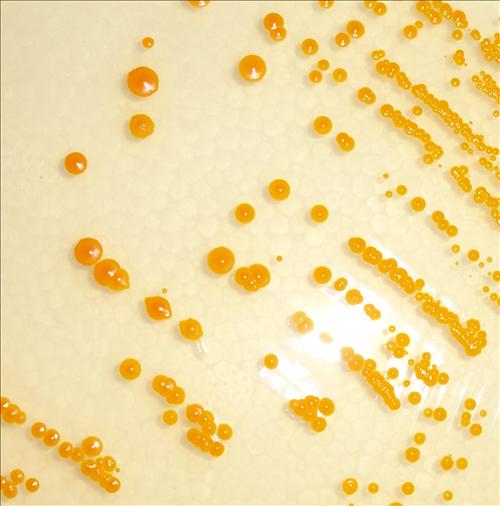

Molecular mechanisms of bacterial pathogenesis; Pseudomonas aeruginosa ocular infections; antibiotic susceptibility testing; biofilms and orthotics
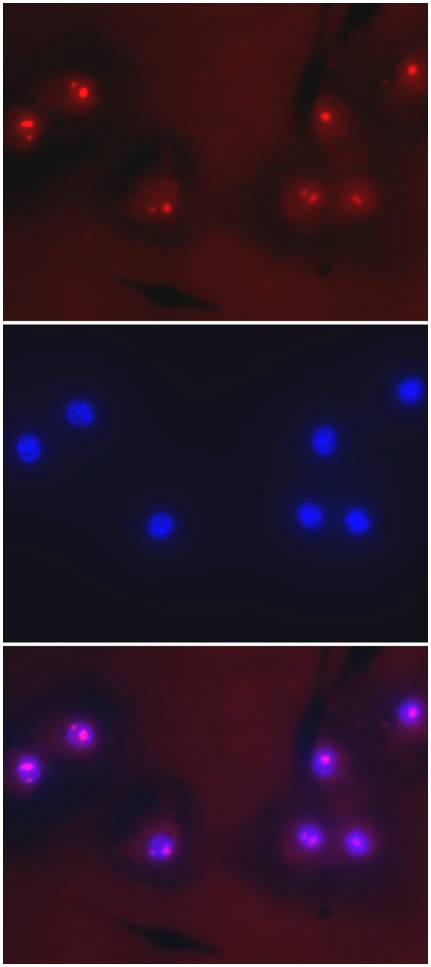

Nona-D-Arginine in Macrophages

 myLSUHSC
myLSUHSC