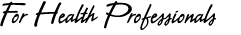
Louisiana Statistics
According to the State of Louisiana Public Health
Office data, there were 139 cases of active TB
cases in 1998 with a case rate of 13.5 /100 K population
in Region 1 (New Orleans Metropolitan area and
surrounding 5 parishes region). This reduced to
110 active cases in 1999, but increased again to
134 active cases in 2000. This data does not include
PPD positive LTB cases and PPD negative contact
cases. It is estimated that 5 % of the population
of Louisiana is PPD positive with latent TB. The
LSU-Wetmore TB Clinic scheduled 1717 TB related
clinic visits in 1999. Eighty eight percent of
the active TB cases are on the DIRECT OBSERVED
TREATMENT (DOT) program with 90% of these cases
undergoing FIELD DOT conducted by DIS workers reaching
these patients at home or at place of work.
Post Katrina Data
View Louisiana Data in MS Excel Spreadsheet
Louisiana Office of Public Health - Tuberculosis Control Program
http://www.dhh.louisiana.gov/offices/?ID=273
TB Update Contemporary Topics in MTB 2010
Download Presentation
The Orleans Parish Triangle of TB
Click here to see larger version of chart
To Be Informed Newsletter
To Be Informed is a newsletter/brochure
in Vietnamese and English based on frequently asked
questions
by
audience
and participants
of the TEACH Program. It is distributed to community
venues and primary care clinics.
Fall/Winter
Discussion Points
Tuberculosis Synopsis Update 2011
- Definition : LTBI, “Chemoprophylaxis”
- Targeted tuberculosis testing in high risk/high prevalence groups and “precision treatment” options
- Three cut-off points for TST (tuberculin skin test) remain
- US Public health Strength of recommendation ABC
- Quality of evidence I II III
- Duration of LTBI Rx: 9 months
- Flexibility based on local public health considerations.
Recent Changes in Emphasis
- Criteria for PPD TST (tuberculin skin test) positivity, by risk stratification
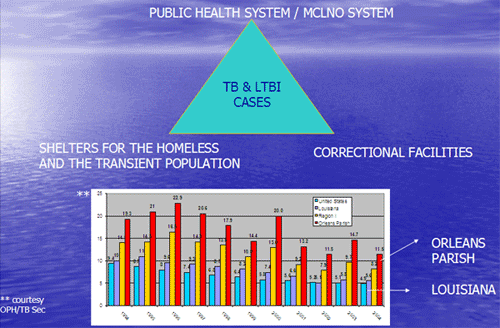
- New
definition of PPD TST (tuberculin skin test) converter: increase
in 10 mm or more within a 2-year period.
- Clinical monitoring
- Lab monitoring in (a) HIV (b)
pregnant (c) postpartum (d) Hx of liver
disease
(e) Those who continue use of alcohol
regularly. (f) Other medical
conditions. For
cessation of Rx on the basis
of LFTs recommended:
Rule of “FASTS” 5
times if asymptomatic; 3 times
if symptomatic
- Intermittent Rx must
be DOPT
- Rifabutin in place of Rifampin in HIV
patients where PI’s are used
- In pregnant
women with HIV or recent contact
history or conversion, treatment should be
started even
in the first trimester.
- In other lower risk
pregnant patients, Rx can be deferred
till after delivery
- Options in INH resistant or PZA intolerant
patients available
- Immune-competent contacts
of MDRTB with LTB, PZA/ETM or PZA/QUIN
for
6 months.
- Immune-compromised contacts of MDRTB…………Rx
for 12 months
Teaching Bullets
- Acid-fast
- Obligate aerobe: Involvement of spleen/heart?
- Intracellular
- Replication time 15-20 hours
- New Colonies generally
do not appear after 6 weeks
- 99% Niacin-positive
- Flouroscient stain more
sensitive than CF stain ( Overall: low
sensitivity with 10000 (10 X4) bact/cc. Quantitatively:
Rare= 3-9/slide;
few =>10/slide;
numerous
1/oil
- PCR: false positive
- DNA probe: rapid but expensive
for ID
- Other AFB = Nocordia,Legionella
Micadei
- 40-70 % of patients with MTB
isolated on culture have positive smears
- Culture
= egg based or agar based
- CXR: nodular=
10x2 –10x4; Cavitary=10x7-10x9
With treatment:
- Within 15 days: TB bacilli decrease
2 log i.e. 10x6 to 10x4
- Cough decreases in
40 % in 1 week and 65 % in 2 weeks
- Drug
regimens that do not include INH do not
render the patient non infectious
as rapidly
- Operational implications regarding infectiousness
should be modified depending
upon living and working conditions.
- Under standard conditions and humidity,
60% survive 3 hours and 30 % survive
9 hours
Rate
of TB:
- 15/1000 close contacts
- 3/1000 - close contacts
Control:
- BCG reduces the growth of organisms in macrophages
- In low incidence areas---endogeneous infection—Rx
LTB
- In high incidence areas—exogeneous
infection---TB control measures
PPD test:
- 48-72 hours –1 week. Plant Day 0 ;
if not read in 7 days, replant 48-72
hours later
- Booster/2 step
| 0 |
2 weeks |
result |
| - |
- |
- |
| - |
+ |
+ Booster Reaction, not conversion |
| + |
|
+ Positive |
- Except in children, the size of the PPD TST (tuberculin skin test) reaction bears no relationship to the
likelihood of active TB.
- BCG induced reactions are smaller and tend to wane more quickly than reactions caused by naturally occurring infections
- History of BCG generally ignored in the US
LTB: Treatment (Chemoprophylaxis)
- 80% reduction in incidence of active TB
- 50% less per year
- Overall 60% reduction
PULM TB
- 35-80 % of patients have fever
- 11% have hyponatremia
- Single early morning specimens have higher yield and lower rate of contamination
than pooled specimens. Increase in yield between 3-5 specimens is low
- Drug resistant mutants: ETH 10x4; INH/SM 10x6;RIF 10x8
- 8-16 % delinquent rates in 6 month DOT
- INH induced hepatitis: 10/1000 ( 0.1-0.3-3%)
- Retrobulbar neuritis with ETH: 15 % with 50mg/kg; 1-5% with 25mg/kg; <1% with 15mg/kg. Increased with renal dysfunction
- 50% of untreated TB patients die within 5 years
- 25% remain chronically ill with positive sputum cultures and infectious
- 25% resolve spontaneously
- Steroids in TB: Cachexia,shock,ARDS,Pericardial disease
- Lymphnode TB: Medical Rx after aspiration better outcome than surgical excision and Rx
- Pleural TB: 30 % have no evidence of pulm lesions on CXR
- Pl Fluid: 10 % eosinophils and 5 % mesothelial cells rules out TB
- POTTS: Two adjacent vertebrae with IV disk ( lower thoracic and upper lumbar)
- CSF : AFB smear 20% +, Culture 50-80%
- TB peritonitis: Active TB uncommon; 50 % have MTB culture positive
- GU TB: 50-70 % have old TB
- 50% of those with pericardial disease have pleural involvement
- Quantiferon TB Gold/TB Spot Test
- Gamma Interferon necessary for activation of microbicidal mechanism in macrophages
- Nitric Oxide: Microbicidal and bacteriostatic
- Murine macrophages which produce NO both inhibit growth and kill virulent human TB bacilli in vitro when activated by TNF alpha and gamma interferon
- Cytokines and lymphokines have the ability to organize granulomas and wall of infection, decrease bacillary load and restrict the mobility of infected macrophages and hence spread of infection
- In immune-deficiency individuals, decreased TNF causes lack of granuloma formation and hence unrestricted spread.
- Caseation necrosis and cavitation is due to killing of TB bacilli with cytokines and T lymphocytes
- MMWR - TIGRA TB Tests June 2010 Update
NTM/MOTT
Who Dat Mott 2011 PowerPoint Presentation
Of all Mycobacteria isolated in 41state labs
- 65% NTM
- 21% MAC
- 5% Mycobacterium kansasii (MyKS)
- MAC in HIV :serotype 4-8
- Rx of MAC in non immune compromised host: 50 % successful with 20 % relapse
Mycobacterium kansasii (MyKS)
- Colonization less frequent than MAC
- 53 % of those from whom MyKS isolated truly had invasive disease
- Same criteria of dx
- 35-40% have no significant lung disease
Rapid growers
- beaded gram positive rods on gram stain
- MyCh/Mfort: Sternal osteomyelitis, mediastinitis,pericarditis,vascular inv, aspiration pneumonitis
- MAC-PD Management Strategy & NTM Summary
For more information regarding NTM/MOTT, please click on the following link:
Nontuberculosis Mycobacteria Info & Research
Contemporary Topics in MTB 2010 through the Wemore TB Clinic Tour
Download Presentation
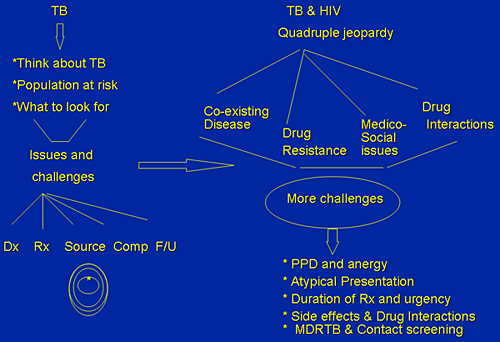
TB & HIV: Quadruple Jeopardy
|




