
Hugh "Houhui" Xia, M.Sc., Ph.D.
Hugh "Houhui" Xia, M.Sc., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Cell Biology and Anatomy
and Neuroscience
Associate Professor, Cell Biology and Anatomy
and Neuroscience
2020 Gravier Street, Suite D
New Orleans, LA 70112
Phone: (504) 568-8524
Fax: (504) 568-5801
hxia@lsuhsc.edu
Degrees
1998-2003: Postdoc, Stanford University
1993-1997: Ph.D., University of California, San Francisco, CA
1989-1992: M.Sc., University of Minnesota, Twin Cities
1984-1988: B.Sc., Peking University, Beijing, China
Bio
2009 - Present: Associate Professor of Cell Biology and Anatomy, and Neuroscience; Neuroscience Center of Excellence, LSU Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, LA
2003 – 2009: Assistant Professor of Cell Biology and Anatomy, and Neuroscience; Neuroscience Center of Excellence, LSU Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, LA
2002-2003: Postdoctoral fellow; Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology, Stanford University, CA
1998-2002: Postdoctoral fellow; Department of Psychiatry, Stanford University, CA
Study Sections
- Ad hoc reviewer for NIH study section SYN on Oct. 2009 and Feb. 2010.
- National Science Foundation grant review (2009).
- Alzheimer's Association (2007).
Awards/Recognitions/Lectures
2006-2008: NARSAD Young investigator award
2004-2006: NARSAD Young investigator award
1999-2002: NRSA Individual Postdoctoral F32 Fellowship, Stanford University
(RC Malenka, Preceptor)
1995: NIH predoctoral training fellow, UCSF (DS Bredt, Preceptor)
1984: Freshman math competition prize, 1984 Peking University, China
Research Interests
Keywords:
molecular mechanisms of synaptic plasticity:
NMDA receptor signaling and CREB mediated gene transcription
Research
NMDA receptor signaling, protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) and CREB mediated gene transcription
Synapse has been shown to undergo persistent modifications in response to different patterns of activity and this change has been hypothesized to underlie the experience-dependent modifications in our brain, including learning and memory. We are interested in how NMDA receptors function in inducing these many forms of synaptic plasticity. We are not only interested in short term modifications in the synaptic protein composition through calcium mediated signaling pathway, but also CREB mediated gene transcription which provides new proteins for long term modification of the synapse. We are in interested in both kinase and phosphatase mechanism of the signaling pathways leading to these changes in the synaptic strength. We use primary hippocampal cultures and hippocampal slices as our model systems. Techniques used include electrophysiological recordings of synaptic transmission, molecular biology for manipulating genes involved in the signaling pathway from NMDA receptor activation to synaptic strength medication and confocal/two-photon microscopy for localization studies of key proteins in these pathways.
Current Research
NMDA receptor signaling, protein phosphatase-1 (PP1)
and CREB mediated gene transcription
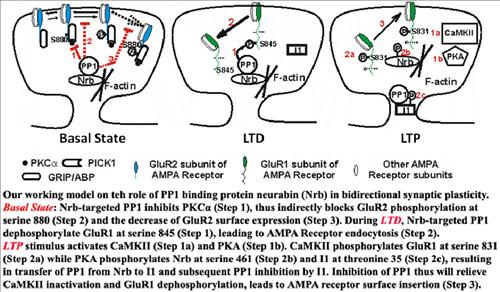
Synapse has been shown to undergo persistent modifications in response to different patterns of activity and this change has been hypothesized to underlie the experience-dependent modifications in our brain, including learning and memory. We are currently focusing on the reversible phosphorylation mechanisms of synaptic plasticity, playing critical roles in both short term modifications in the synaptic protein composition (see schematics below) and in CREB mediated gene transcription process which provides new proteins for long term modification of the synapses. We use primary hippocampal cultures and organotypic hippocampal slice culture as our model systems to address these questions. Techniques used include electro-physiological recordings of synaptic transmission, molecular biology for manipulating genes involved in the signaling pathway from NMDA receptor activation to synaptic strength medication and confocal/two-photon microscopy for localization studies of key proteins in these pathways. The results from our study will provide insights in therapeutic interventions in many diseases in which synaptic functions are compromised, for example, mental retardation and epilepsy.
Selected Publications
Key Recent Papers:
Yang H., Hou H., Pahng A., Gu H., Nairn A.C., Tang Y.P., Colombo P.J. and Xia H. Protein phosphatase-1 inhibitor-2 is a novel memory suppressor.Journal of Neuroscience (2015) Nov 11; 35(45):15082-15087.
Hou H., Chávez A.E., Wang C.C., Yang H., Gu H., Sidddoway B.A, Hall B.J., Castillo P.E. and Xia H.The Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 suppresses CREB signaling by targeting NMDA receptor function. Journal of Neuroscience (2014) Oct 15; 34(42):14006-14012. PMID: 25319697
Siddoway, B.A., Hou, H., Yang, J., Sun, L., Yang, H., Wang, G. and Xia, H. Potassium channel Kv2.1 is regulated through protein phosphatase-1 in response to increases in synaptic activity. Neuroscience Letter (2014) Sep 8;583C:142-147.
Siddoway, B.A., Hou, H., Xia H. Molecular mechanisms of synaptic downscaling.Neuropharmacology(2014) Mar, 78:38-44. PMID: 23911745.
Siddoway B., Hou H., Yang H., Petralia R.S. and Xia H Identification of a bidirectionally-regulated, sequence-specific phosphoproteome in mammalian neurons that regulates protein expression. Journal of Neurochemistry (2014) Mar, 128(6):841-51. PMID: 24117848.
Hou H., Sun L., Siddoway B., Petralia R.S., Yang H., Gu H., Nairn A. and Xia H. Synaptic NMDA receptor stimulation activates PP1 by inhibiting its phosphorylation by Cdk5. Journal of Cell Biology(2013) Nov. 11, 203(3). PMCID: PMC3824016
Our work was highlighted in the JCB: http://jcb.rupress.org/content/early/2013/10/28/jcb.2033iti3
 Moreover, AAAs and EurekAlert has sent out a Public release regarding our work:
Moreover, AAAs and EurekAlert has sent out a Public release regarding our work:
http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2013-11/rup-lam103113.php#
Siddoway B., Altimimi F.H., Hou H., Petralia R., Stellwagen, D. and Xia H. An essential role of inhibitor-2 regulated protein phosphatase-1 in synaptic downscaling. Journal of Neuroscience(2013) July 3, 33(27):11206-11211. PMCID: PMC3718377.
Siddoway, B., Hou, H., Xia H. Glutamatergic Synapses: Molecular organization. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences(2011), DOI: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0000235.pub2.
Dong C., Yang L., Zhang X., Gu H., Lam M.L., Claycomb W.C., Xia H., Wu G. Rab8 interacts with distinct motifs in a2B- and b2-adrenergic receptors and differentially modulates their transport.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 27, 285: 20369-20380 PMCID: PMC2888448
Gao, J., Siddoway, B., Huang, Q., Xia, H: Inactivation of CREB mediated gene transcription by HDAC targeted protein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 379:1-5.
Hu, X.D., Huang, Q., Yang, X., Xia, H: Differential regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking by neurabin-targeted synaptic protein phosphatase-1 in synaptic transmission and long-term depression in hippocampus Journal of Neuroscience(2007) 27:4674-86.
Hu, X.D., Huang, Q., Roadcap, D.W., Shenolikar, S.S., Xia, H: Actin-associated neurabin-protein phosphatase-1 complex regulates hippocampal plasticity. Journal of Neurochemistry(2006) 98:1841-51.
Deisseroth, K., Mermelstein, P.G., Xia, H. and Tsien, R.W: Signaling from synapse to nucleus: the logic behind the mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol (2003) 13:76-80.
Xia, H., von Zastrow, M., Malenka, R.C: A novel anterograde trafficking signal present in the N-terminal extracellular domain of ionotropic glutamate receptors. J Biol Chem (2002) 277:47765-47769.
Braithwaite, S., Xia, H., Malenka, R.C: Differential Roles of NSF and GRIP in AMPA receptor cycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2002) 99:7096-7101.
Morishita, W., Connor, J.H., Xia, H., Quinlan, E., Shenolikar, S., Malenka, R.C: Regulation of synaptic strength by protein phosphatase 1 Neuron(2001) 32:1133-1148.
Xia, H., Hornby, Z.D., Malenka, R.C: An ER retention signal explains differences in surface expression of NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits. Neuropharmacology (2001) 41:714-723.
Selected Papers:
Gao, J., Hu, X.D., Xia, H: Neurabin is a PKA substrate critical for LTD induction.
(manuscript in preparation)
Huang, Q., Lee, I-P., Medina, V., Xia, H: Structural determinant in cycloxygenase-2 in its nuclear envelope and ER localization. (manuscript in preparation)
Gao, J., Siddoway, B., Xia, H: Differential effects of neurabin and spinophilin in spine maturation. (manuscript in preparation)
Carroll, R.C., Beattie, E.C., Xia, H., Lscher, C., Altschuler, Y., Nicoll, R.A., Malenka, R.A., von Zastrow, M: Dynamin-dependent endocytosis of ionotropic glutamate receptors, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (1999) 96:14112-14117.
Xia, H., Fitzgerald, J., Bredt, D.S., Forsayeth, J.R: Detection of mycoplasma infection of mammalian cells, Biotechniques (1997) 22:934-936.
Brenman, J., Xia, H., Chao, D., Black, S., Bredt, D.S: Regulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase through alternative transcripts, Dev Neurosci(1997) 19:224-231.
Chao, D.S., Silvagno, F., Xia, H., Cornwell, T.L., Lincoln, T.M., Bredt, D.S: Nitric oxide synthase and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase concentrated at the neuromuscular endplate, Neuroscience (1997) 76:665-672.
Xia, H., Winocur, S., Kuo, W., Waltherr, M., Bredt, D.S: Actinin-associated LIM protein: identification of a domain interaction between a PDZ motif and spectrin-like repeat, J Biol Chem(1997) 139:507-515.
Brenman, J.E., Chao, D.S., Gee, S.H., McGee, A.W., Craven, S.E., Santillano, D.R., Wu, Z., Huang, F., Xia, H., Peters, M., Froehner, S.C., Bredt, D.S: Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and alpha1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains, Cell(1996) 84:757-767.
Holtzman, D.M., Lee, S., Li, Y., Chua-Couzens, J., Xia, H., Bredt, D.S., Mobley, W.C: Expression of neuronal-NOS in developing basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: regulation by NGF, Neurochem Res(1996) 21:861-868.
Silvagnano, F.*, Xia, H.*, Bredt, D.S: Neuronal nitric oxide synthase-m, an alternatively spliced isoform uniquely expressed in differentiated skeletal muscle, J Biol Chem (1996) 271:11204-11208.
Xia, H., Bredt, D.S: Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase proteins, Meth Enzymol(1996) 268:427-436.
Brenman, J., Chao, D., Xia, H., Aldape, K., Bredt, D.S: Nitric Oxide synthase complexed with dystrophin in skeletal muscle and absent from skeletal muscle sarcolemma in Duchenne muscular dystrophy,Cell (1995) 82:743-752.
Additional Info
Funding
“Inhibitor-2 is a positive regulator for PP1's synaptic
and cognitive functions”
Principal Investigator: Houhui Xia, Ph.D.
Agency: NIMH/NIH (1R01MH109719-01)
Period: 04/05/2016-01/31/2021
“The role of protein phosphatase-1 inhibitor-2 in synaptic scaling”
Principal Investigator: Houhui Xia, Ph.D.
Agency: National Science Foundation (NSF) IOS-# 1457336.
Period: 8/15/2015-8/14/2018.

 myLSUHSC
myLSUHSC