December 2023 Case
AN INCIDENTAL PELVIC MASS IN A PATIENT WITH SHORTNESS OF BREATH
Contributors: Asra Feroze, MBBS, Michael Morin, MD and Jonathan Somma, MD
A female patient in her eighties with a past medical history of aortic stenosis, congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and benign hysterectomy (details unknown) was brought to the emergency room due to shortness of breath. She was evaluated and managed for an exacerbation of congestive heart failure. Non-contrast abdominal computed tomography study (CT) identified an incidental, indistinct, approximately 10.0 x 8.0 x 7.0 cm lesion in the mid pelvis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with contrast (Figure 1) revealed a maximally 9.6 cm, lobulated, solid, heterogeneous mass distinct from the large bowel and bladder. Small bowel loops contacted the margins of this mass, but there was no clear evidence of small bowel involvement or of proximal small bowel obstruction.
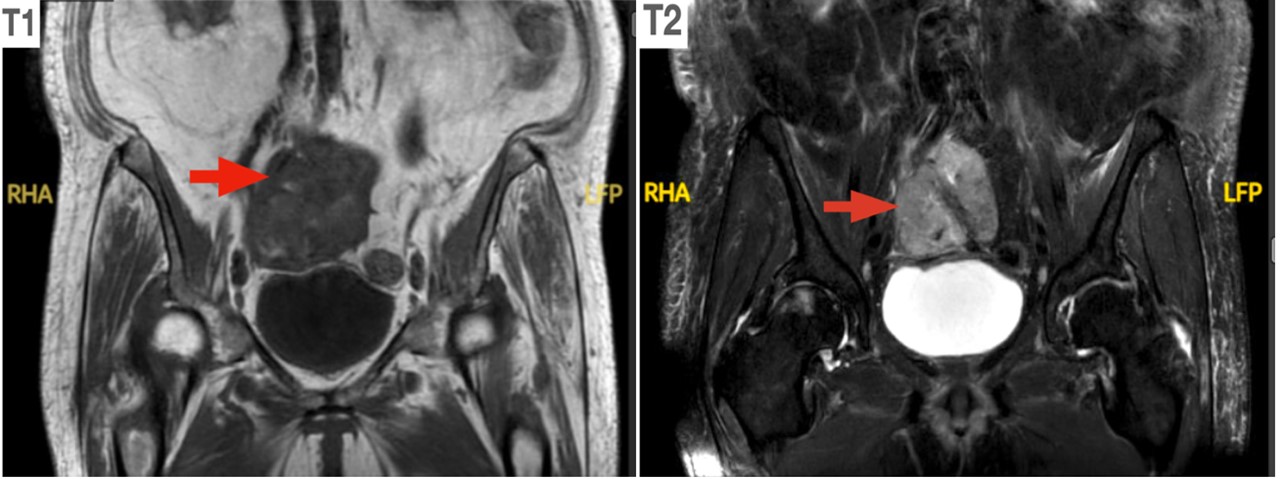
Figure 1. MRI showing T1 and T2 weighted contrast images (red arrow indicates mass)
A lesion of mesenteric origin versus an adnexal one was considered. Given the patient’s age, poor health status and difficult access site of the lesion, a tissue biopsy could not easily be performed. However, an image-guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) was performed, and aspirate smears stained with Diff-Quik (Figure 2) and Papanicolaou (Figure 3) were prepared. Also, a cell-block was prepared from the sample obtained, and sections from this were used for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (Figure 3) as well as immunochemical staining (Figure 4).
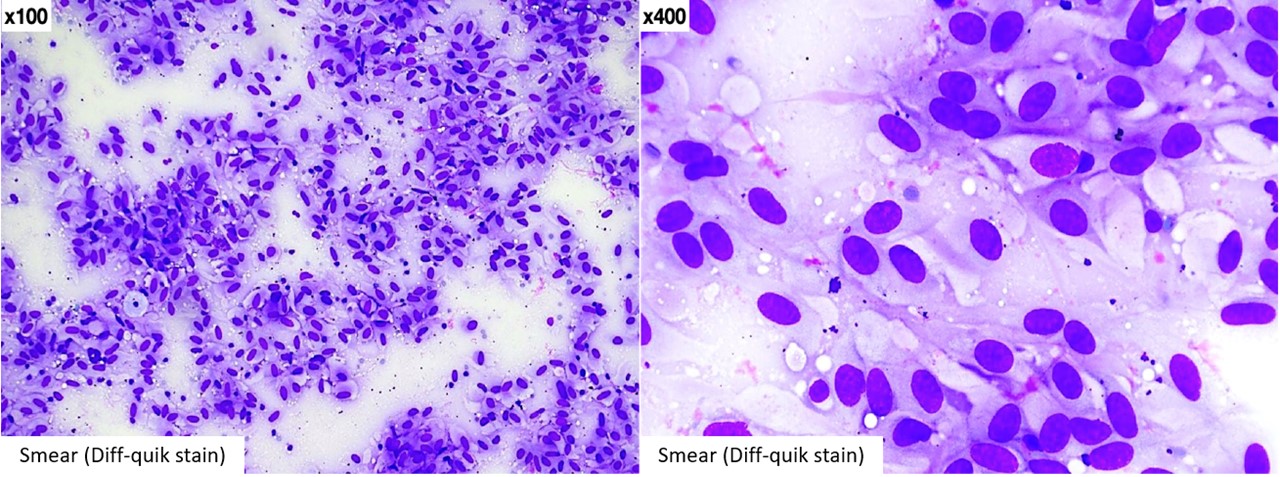
Figure 2
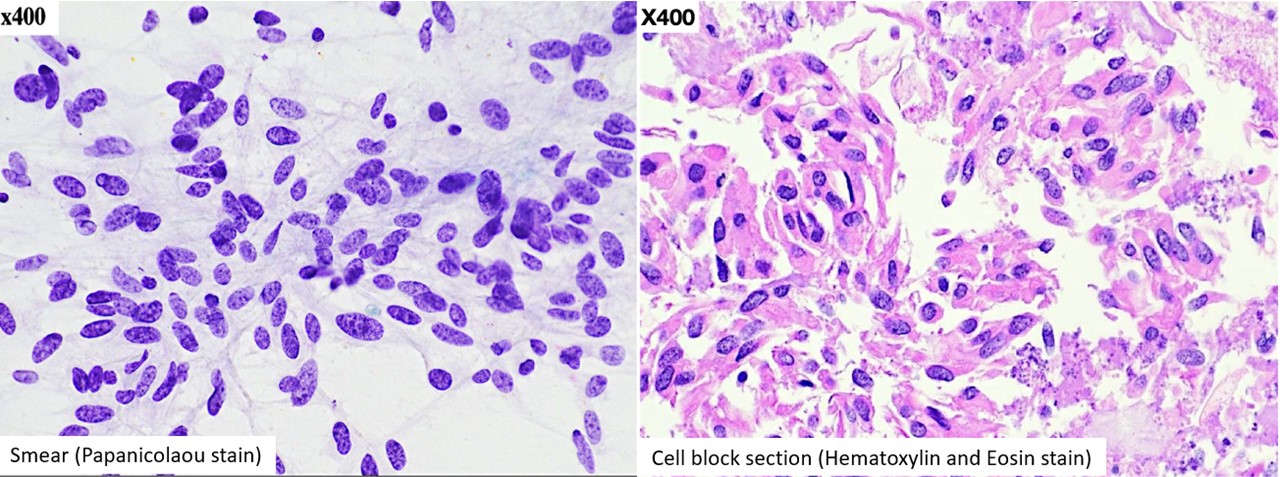
Figure 3
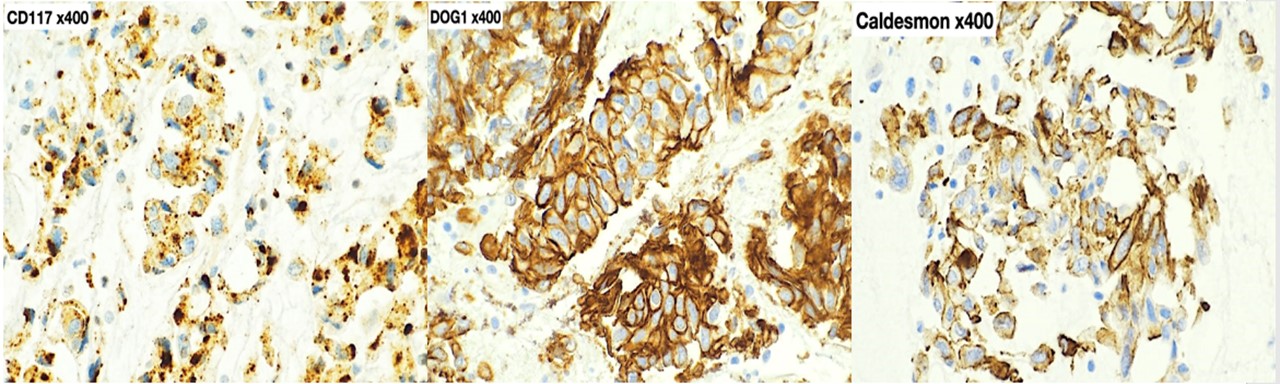
Figure 4
Additional immunochemical stains showed focal immunoreactivity for SMA (smooth muscle actin), while desmin, S100, CD34, STAT6, calretinin, inhibin, and HMB45 were all negative in the lesional cells.
QUESTION:
Based on the above cytology and immunohistochemical staining profile, what is the most likely diagnosis?
- Leiomyoma
- Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- Schwannoma
- Solitary fibrous tumor
- Fibrothecoma
Click here for answer and discussion
